Cool Javascript snippets to know 15th July 2024

1) Reverse a string
const reverseTheStr=(str)=>str.split(" ").reverse().join(' ');
reverseTheStr("This is good");// good is This
2) Capitalize First Character
const capitalizeFirstChar = str =>str.charAt(0).toUpperCase() +str.slice(1);
console.log(capitalize("manju"));// Manju
3) Capitalize First Letter Of Each Word. Also called Title casing
const capitalizeFirstLetterOfEachWord= sentence => sentence.replace(/\b\w/g, char => char.toUpperCase());
capitalizeFirstLetterOfEachWord("nice world"); // Nice World
Wondering what the regex does? Quick crash course
- \b a word boundary assertion, which matches positions where a word character is next to a non-word character.
- \w matches any word character (equivalent to [a-zA-Z0-9_]).
- The g flag at the end of the regular expression indicates that the replacement should happen globally throughout the string.
4) Tired of using console.log everywhere and want something shorter
const sl=console.log.bind("document");
sl("hello world")
5) Normal function and want to write the same method the smarter way?
Old way
function test(){
console.log("hello test- I am called the old way")
}
test();
const newTest=()=> console.log("hello test- I am called the new way");
test();
we can make it more compact by what we learnt so far (using number 4 above)
newTest=()=> sl("hello test- I am called the new way");
newtest()6) Single/Multiple Replace
//Replace Single
const replaceSingleHello="Hello Nice World.Hello winter";
replaceSingleHello.replace(/Hello/,"Hi");//Hi Nice World.Hello winter
//Replace Multiple
const replaceAllHello="Hello Nice World.Hello winter and Hello Summer";
replaceAllHello.replace(/Hello/g,"Hi");//Hi Nice World.Hi winter and Hi Summer
7) Number to string and other way round
//number to string. Use +=
let data=1;
console.log(typeof(data)); //number
data+=" am string"
console.log(typeof(data)+" ** "+data); //string ** 1 am string
//string to num. Use =+
let strNum="2";
let strNum1=+strNum+2;
console.log(strNum1);// 4
console.log(typeof(strNum1));//number
8) Get last 2 elements from array
const getLastTwoFromArray = (nums) => nums.slice(-2);
console.log(getLastTwoFromArray([2, 3, 1, 4, 5])); //[4,5]
8) Get the last occurenence of an item in an array
const getLastItem = (nums, item) => nums.lastIndexOf(item);
console.log(getLastItem([2, 3, 1, 4, 1, 5], 1)); //4
9) Randomize Arrays
const jumbleArrays = (names) => names.sort(() => Math.random() - 0.5);
console.log(jumbleArrays(["advin", "harry", "peter", "sunny"]));// will print names in random order
10) Populate an array with default values
Lets think of a scenario. Say you are creating an application that displays a list of components .You can control the visibility of these components with a flag.Say for eg hidden flag .To start with you want this flag to be false. Lets see how we can achieve that in 2 differnt ways i.e the old and new way
Old way
let uiComponents = 4;
let uiComponentFilledArray = [];
for (let i = 0; i < uiComponents; i++) {
uiComponentFilledArray[i] = { hidden: true };
}
console.log(uiComponentFilledArray);//prints all elements with hidden true
let uiComponents = 4;
let uiComponentFilledArray = [];
let uiComponentFilledNewArray = new Array(uiComponents)
.fill(null)
.map(() => ({ hidden: false }));
console.log(uiComponentFilledNewArray);
Wondering what fill does?
The new Array creates an array of arraySize length, but the elements are empty slots, not filled with any value, even not undefined.The map() function in JavaScript only operates on elements that have values (even undefined), but it does not operate on empty slots. Therefore, uiComponentFilledNewArray will be an array of empty slots and we cannot use map() on it.In order to achive what we want, we need to ensure each element is mapped correctly, you should use fill() before map(), as in your original example.
10a) Populate array with default values
Similar to above,but here we initialize the array with default values and not an object
let defaultIntArray = new Array(4).fill(0);
console.log(defaultIntArray);//[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
11) Ternary operator for conditional assignment
Below am using ternary operator for conditional assignment. Bascially am checking if you have paid then you are allowed an entry ????The expression isPaid === true checks if isPaid is equal to true. If true, allowEntry is set to "yes"; otherwise, "no". This is a concise way to handle conditional logic in JavaScript.
let isPaid = true;
let allowEntry = isPaid === true ? "yes" : "no";
console.log("You are allowed:" + allowEntry);//You are allowed:yes
12) Using reduce instead of a traditional foreach loop
Say you have an array of JSON object with each object having an id and the orderId. I want to return an object with key as the user id and all the orders that user made. I have created some dummy data that will be used for this egample. I have hosted the same in "my-json-server.typicode.com". The link to the dummy data is
I have added images below how we want to tranform it. On left is the initial data and on right is the transformed data
Initial Data
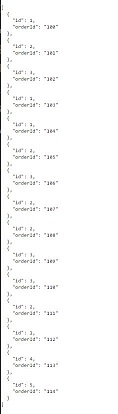
Transformed Data

fetch(
"https://my-json-server.typicode.com/manjusa/jsonserver_typicode_demo/customerOrder"
)
.then((resp) => resp.json())
.then((orders) => {
const userOrders = {};
orders.forEach((order) => {
if (userOrders[order.id]) {
userOrders[order.id].push(order);
} else {
userOrders[order.id] = [order];
}
});
console.log(userOrders);
});
fetch(
"https://my-json-server.typicode.com/manjusa/jsonserver_typicode_demo/customerOrder"
)
.then((resp) => resp.json())
.then((orders) => {
const userOrders = orders.reduce((acc, order) => {
if (acc[order.id]) acc[order.id].push(order);
else acc[order.id] = [order];
return acc;
}, {});
console.log(userOrders);
});
13)Arrays to Objects
Old Way
let weekdays = ["sunday", "Monday", "tuesday", "Wed"];
let result = {};
weekdays.forEach((day, index) => (result[index] = day));// { '0': 'Sunday', '1': 'Monday', '2': 'Tuesday', '3': 'Wednesday' }
let weekdays = ["sunday", "Monday", "tuesday", "Wed"];
let newResult = { ...weekdays };//{ '0': 'Sunday', '1': 'Monday', '2': 'Tuesday', '3': 'Wednesday' }
14)Objects to Arrays
Old Way to get all the Keys from an Object
let person = { Name: "David", Age: 20, Location: "Melbourne", Level: 1 };
let personKeys = [];
for (var key in person) {
personKeys.push(key);//[ 'Name', 'Age', 'Location', 'Level' ]
}
let person = { Name: "David", Age: 20, Location: "Melbourne", Level: 1 };
let personKeys = Object.keys(person);//[ 'Name', 'Age', 'Location', 'Level' ]
let person = { Name: "David", Age: 20, Location: "Melbourne", Level: 1 };
let personValues = Object.values(person);//[ 'David', 20, 'Melbourne', 1 ]
let personEntries = Object.entries(person);
//personEntries will print: [
[ 'Name', 'David' ],
[ 'Age', 20 ],
[ 'Location', 'Melbourne' ],
[ 'Level', 1 ]
]
15)Calculate number of days given two dates
16) Given a date, get me the day of the year
17) Reduce Function to Separate Odd and Even Numbers in an Array
Email me at "techspacedeck@gmail.com" incase you have queries. Alternatively, you can fill the "CONTACT" form or drop a comment below